Milestone
Robotic Manipulation | PI Control | Omnidirectional Robot | Python | Motion Planning |
Demonstration
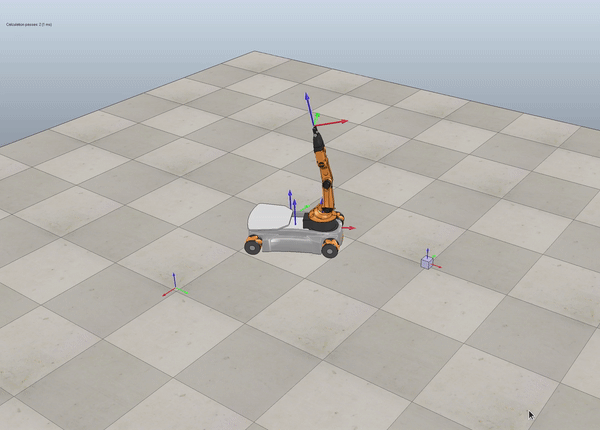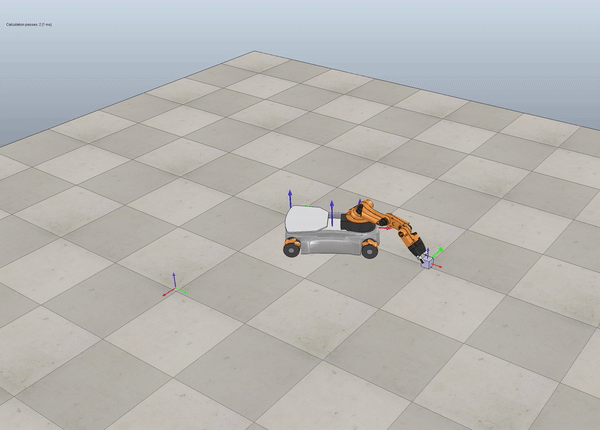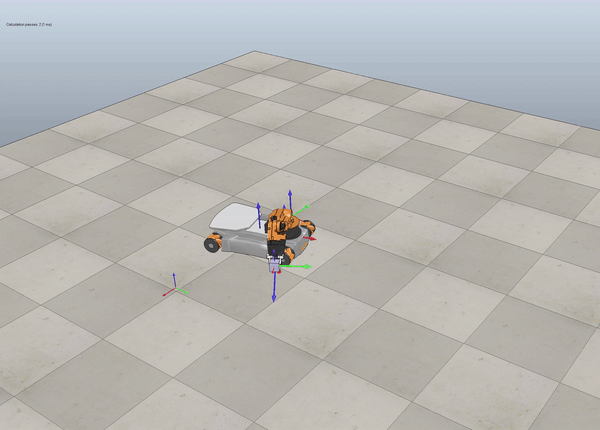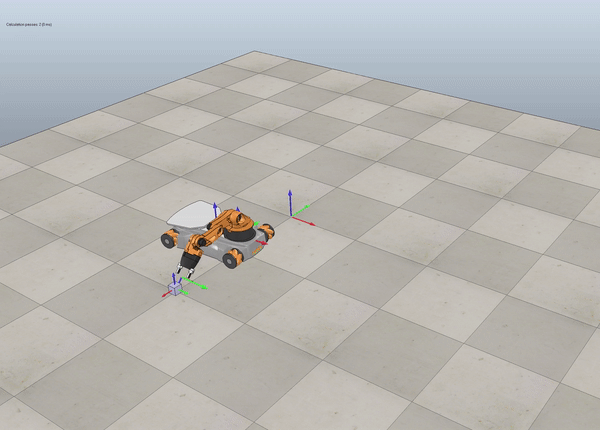
Description
In this project, I wrote a software that plans a trajectory for the end-effector of the YouBot mobile manipulator, The goal is to pick a small box from a known location and place it on a specific position & orientation.
Overview
The YouBot is an omnidirectional mobile robot with a 5-DOF robotic arm, simulated in CoppeliaSim simulation software. The project is split into 3 main parts:
- Generate trajectory for end-effector given the cube initial,desired position (see figure 1).
- Next state , given the current velocity of all joints and wheels calculate the next configuration state.
- Feedforward PI control where we calculate the joint velocities given the current state and the reference trajectory path.
Generate trajectory
In order to generate the reference trajectory for the end-effector frame I used six concatenated trajectory segments, as described above.
- A trajectory to move the gripper from its initial configuration to a "standoff" configuration a few cm above the block.
- A trajectory to move the gripper down to the grasp position.
- Closing of the gripper.
- A trajectory to move the gripper back up to the "standoff" configuration.
- A trajectory to move the gripper to a "standoff" configuration above the final configuration.
- A trajectory to move the gripper to the final configuration of the object.
- Opening of the gripper.
- A trajectory to move the gripper back to the "standoff" configuration.
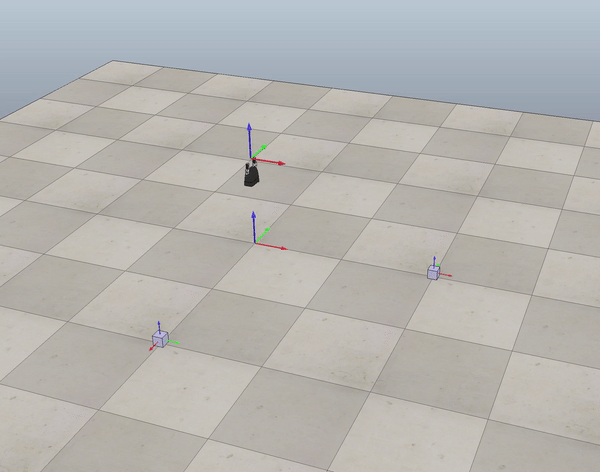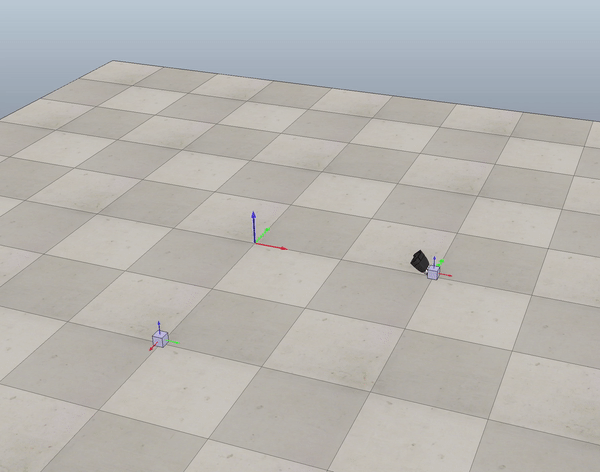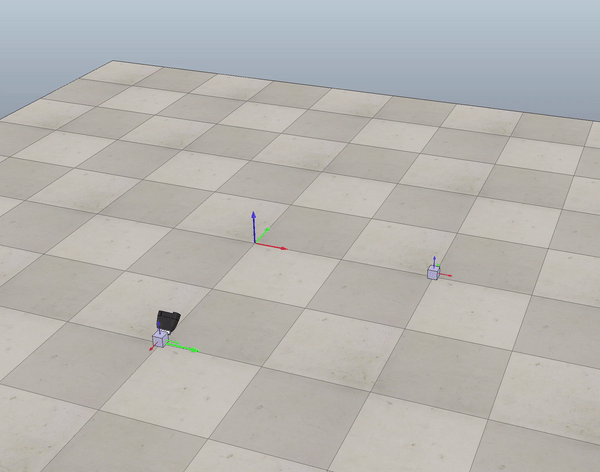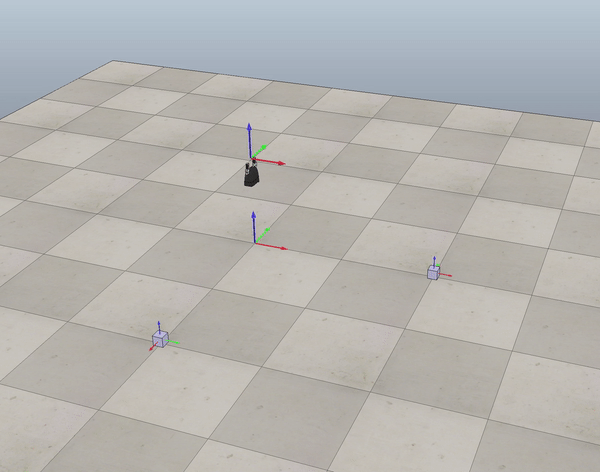
Fig. 1 end-effector trajectory
The Next State part is basically our update function going from time t to t + Δt using the first-order Euler step.
- new arm joint angles = (old arm joint angles) + (joint speeds) * Δt
- new wheel angles = (old wheel angles) + (wheel speeds) * Δt
- Since YouBot is equipped with omnidirectional we calculate the chassis velocity from figure 3.
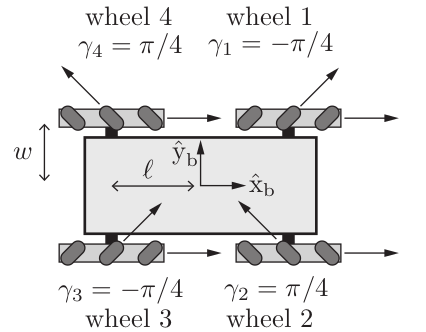
Fig. 2 omnidirectional wheels of YouBot
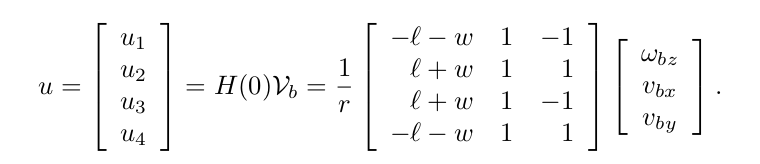
Fig. 3 chassis velocity
Feedforward PI control
Our controler is described by equation at figure 4, we used only Position and Integration. At figure 5 we see the error of the end-effector and chassis relative to time.
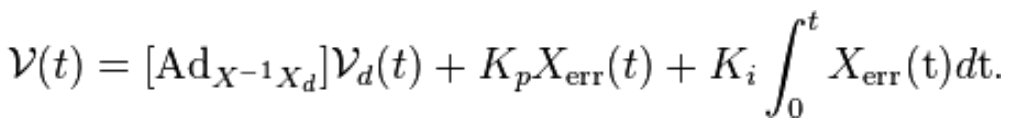
Fig. 4 control equestion
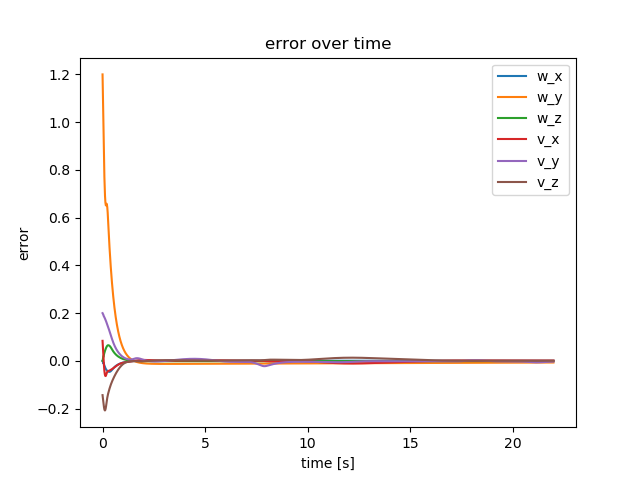
Fig. 5 controler error
Results
Below we see some examples of YouBot in Coppelia Simulator.
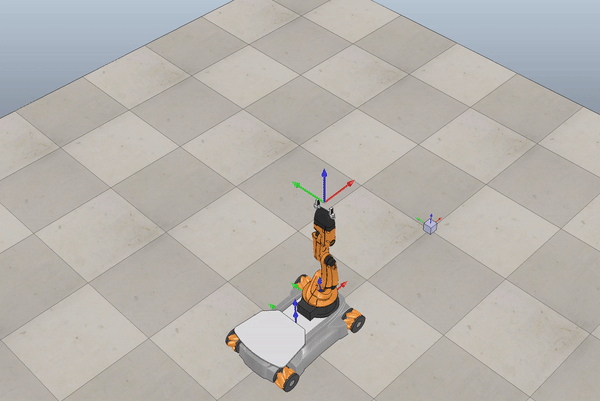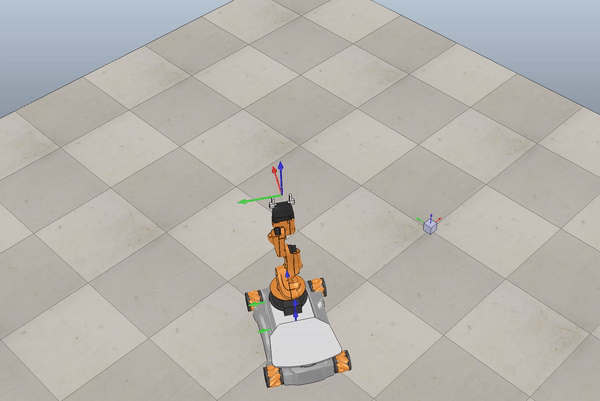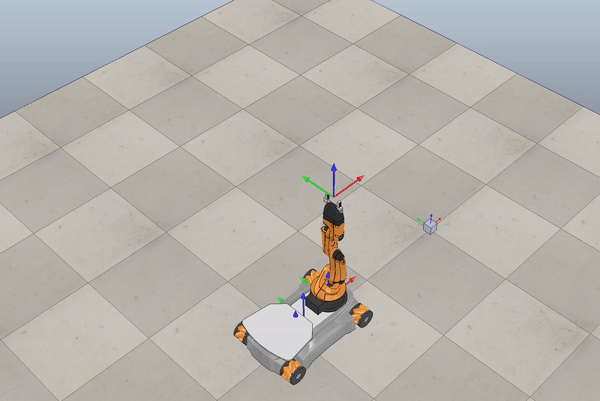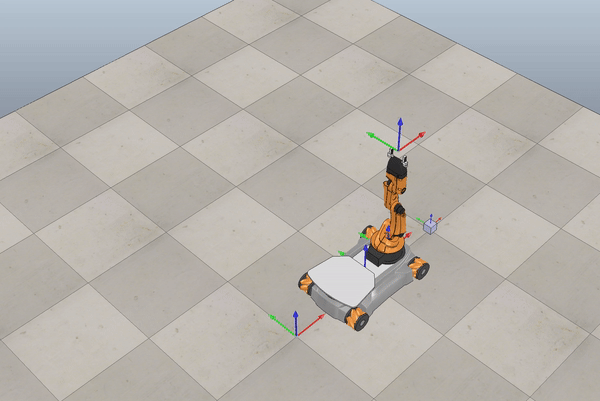
Fig. 6 Example omnidirectional wheels movement

Fig. 7 Final example pick and place box